
www.flinturology.com
Urology Services, Inc.
G-1121 West Hill Rd.
Flint, Michigan 48507
Tel: 810.232.8888
Fax: 810.232.9190
Email: jbauer@flinturology.com
[map]
 |
John J. Bauer, M.D.
www.flinturology.com Urology Services, Inc.
|
Contents
General information
Pre-operative instructions
Risks and Complications
Detailed Surgery Description
Family waiting instructions
Post-operative instructions
Printing tip: If you want to print only one portion of this entire document, you should be able to do this depending on your software. To print a selection, highlight the section you want to print using your mouse, then click on print, and then in the print menu, choose "selection."
Terminology tip: If you come across words you don't understand, look them up in the On-Line Medical Dictionary.
Penile Implants
The penile prosthesis is a device that is surgically implanted inside the body. Implants are most successful for men who can ejaculate and have orgasms even though they can't achieve erections. All penile implants place prosthetic inner tubes within the penis to mimic the inflation process and create an erection. Used since the 1950s, thousands of men have been treated successfully with implants and there have been many advances in the technology.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Implants
Implants are effective in treating almost any type of impotence. They have a 90% success rate when both partners are informed about these prostheses and their limitations. Prostheses don't require follow-up treatment after implantation and no medicines or injections are necessary. In addition, once the prosthesis is in place and functioning, there are no additional costs. The newer prostheses are very reliable, with a chance of mechanical failure in the range of only 2% to 4 % per year.
However, surgical implants permanently change the internal structure of the penis. If the prosthesis is ever removed, normal erections rarely return. There is a small (3% to 5%) chance of infection that could require removal of the prosthesis. Some patients can develop surgical complications or anesthetic complications. Occasionally, patients will notice numbness at the head of the penis and intercourse can be uncomfortable.
Because the erection is not caused by increased blood flow to the penis, the head of the penis is not part of the erection, and this softness may bother some men.
Inflatable Penile Prosthesis
Inflatable prostheses are the most natural-feeling of the penile implants, because the penis can be either erect or flaccid. These implants are made of two soft inner tubes silicone or bioflex, which are inert plastics. The tubes are filled with a sterile liquid that comes from a small reservoir placed under the muscles of the abdomen. A pump in the scrotum is used to move the fluid from the reservoir to the tubes. The more fluid that is pumped into the inner tubes, the firmer and larger the erection. When the erection is no longer desired, the fluid returns to the reservoir, leaving the penis once again soft. (See Figure)
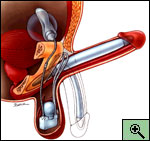
See also: American Medical Systems, Inc. (AMS)
Video Demonstrations
One major disadvantage of this type of device is that the surgical procedure to implant this type of device is slightly more complicated than for a semi-rigid implant. Also, because there are more mechanical parts, there is a higher chance of mechanical failure that would require repairs or adjustments.
Many insurance companies cover part or all of the costs of the prosthesis replacement but not the surgical or hospital fees.
The options regarding the penile prosthesis are malleable, self-contained inflatable and this multi-piece inflatable product. Please see the links to the other procedures for comparison.
Your pre-operative appointments
Before your surgery, you will be seen by the physician and the anesthesiologist, and when applicable, there is a pre-admission appointment with the hospital. Click here to read more details about these appointments, referred to as the Pre-Operative Work-Up.
Change In Health Status
Notify your surgeon if you experience any significant change in your health status: develop a cold, influenza, a bladder infection, diarrhea, or other infection, before your surgery.
Pre-Operative Medication Instructions
Unless specifically instructed otherwise by your surgeon or anesthesiologist, please observe the following guidelines for taking your medicines before surgery:
As injury to the bowel is unlikely in this procedure, you will have the simplest form of a bowel preparation, described below.
Pre-Operative Diet Instructions
Unless specifically instructed otherwise by your surgeon or anesthesiologist, patients of all ages must observe the following diet restrictions before surgery:
Patients undergoing operative or diagnostic procedures involving sedation are required to refrain from eating, drinking or taking anything by mouth for a stated period prior to their surgery or procedure. The reason for this is to prevent complications caused by nausea or vomiting while you are unconscious. Should you vomit while in the unconscious state, the risk exists that the vomit may enter into your lungs causing serious complications such as pneumonia. These complications may result in an extension of your hospitalization following your surgical procedure. It is for this reason patients are often instructed to have nothing by mouth after midnight the night prior to your operation unless otherwise instructed by an anesthetist.
Pre-Operative Cleaning Instructions (bathing and showering instructions)
Pre-operative showers are to be taken the night before and the morning of surgery just prior to your arrival. All adults are required to take a shower using either a Betadine or Hibiclens Surgical Scrub antibacterial soap. The reason is to remove as much bacteria from your skin as possible prior to your surgery. If you are allergic to these products please notify your physician or nurse. Perform your shower as follows:
On The Day Of Surgery
The anesthesiologist will discuss with you the anesthetic most appropriate for your medical condition and procedure prior to surgery.
After your surgery you must be escorted/driven home by a responsible adult. You may take a taxi car or shuttle if accompanied by a responsible adult who can stay with you after the driver departs.
Time To Arrive For Your Surgery
During your Pre-Admission Interview, our Registered Nurse will provide you with the correct time to arrive for check-in prior to your surgery.
ARRIVAL TIME:
WHERE TO ARRIVE:
The risks and complications for this surgery are described in the "Counseling and Pre-Op Note" that you will need to sign before the surgery. The main content of that note is listed below.
Indications:
Patient is a male who is scheduled to have placement of a penile prosthesis. This operation is most often performed for severe erectile dysfunction and allows a patient to have an erection, which is usable for sexual intercourse.
Alternatives:
Alternatives to the procedure include observation; oral agents such as sildenafil, trazadone, and yohimbine; pharmacological injection programs (alprostadil, papaverine, phentolamine and combinations); vacuum tumescence devices; intra-urethral therapy (alprostadil); and behavioral/sexual therapy. Several types of penile implants are available: malleable, semi-rigid; self contained inflatable; and multi-piece inflatable with connectors.
Risks/Complications:
The risks and complications of the procedure where extensively discussed with the patient. The general risks of this procedure include, but are not limited to bleeding, transfusion, infection, wound infection/dehiscence, pain(short and long term), scaring of tissues, failure of the procedure, potential injury to other surrounding structures, deep venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolus, myocardial infarction, heart failure, stroke, death or a long-term stay in the Intensive Care Unit (ICU). Additionally, mentioned were the possible serious complications of the anesthesia to include cracked teeth, airway damage, aspiration, pneumonia, spinal head-ache, nerve damage, spinal canal bleeding and malignant hyperthermia. Your anesthesiologist will discuss the risks and complications in more depth separately. Additional procedures may be necessary.
The specific risks of this procedure include, but are not limited to: prosthetic infection requiring long term treatment with antibiotics, penile/urethral injury, removal of prosthetic secondary to erosion or infection, inability to place a specific type of prosthetic (inflatable vs. semi-rigid) requiring the placement of an alternative type, prosthesis failure/breakage/leakage requiring future revision/removal/ replacement, altered cosmetic appearance, perforation of the cura, crossed rods, delayed climax and spontaneous erections. With a prosthetic device you will be required to take prophylactic antibiotics before any other surgical or dental procedures to prevent possible bacterial seeding and infection of you prosthetic. The glans penis may droop (SST deformity) after surgery or after some use of the prosthesis during intercourse.
It is also vitally important to have realistic expectations of the surgery. The penile prosthesis does not give the same type "normal" erection, but acts as a device to increase the penile rigidity for intercourse. You may be dissatisfied with the appearance and size of the penis after the surgery. This procedure will not give you increased length and girth.
You understand the procedure, general and specific risks as discussed and agree to proceed with the procedure. You also understand that not every possible complication can be listed in this counseling note and additional risks are possible, although unlikely.
To view the actual printable form for this surgery, click here: Counseling Note for AMS Inflatable 3-Piece Prosthesis. To print the document, simply select print after you have opened the page. You can use that copy to sign before your surgery.
Terminology tip: If you come across words you don't understand, look them up in the On-Line Medical Dictionary.
Indications: Male patient with ImpotenceSample Procedure Dictation:
The patient was given general anesthesia / spinal anesthesia, placed in the supine position and then prepped and draped in the usual standard sterile manner. A 16 Fr Foley catheter was placed per urethra and the bladder was drained. A transverse penoscrotal incision was made through the skin and dartos layers to expose the interscrotal tissues. A space was made with blunt dissection between the testicles to expose the corpora cavernosa bilaterally and the corpora spongiosum. The Foley catheter was palpated to identify the urethra. This structure was avoided for the remaining portion of the case. Care was taken not to dissect down the midline were the urethra was located. Multiple stay sutures were placed for retraction and a 2-3 cm vertical incision was made in the corpora using a #12 blade (hook). A metzenbaum scissors was used to develop a space just under the tunica albugenia in both directions to allow sequential dilation of the corpora with Hagar dilators starting with an 8 mm up to a 14 mm. The dilators were completely seated in the proximal dilation and noted to be in the mid-glans in the distal dilation. The corporal lengths were then measured in both directions and the total intercorporal length was documented: Right ___cm, Left ___cm. Using the total intercorporal length and the company-sizing chart, it was determined that a 12mm diameter and ___cm long cylinder was required with proximal tip lengths of: Right proximal __cm and Left proximal ___cm. The corpora were copiously irrigated with GU irrigant prior to placement of the prosthesis cylinders with tips. The cylinders, proximal tips, pump and the 70cc / 100 cc reservoir were soaked in GU antibiotic solution. All the air was irrigated from the cylinders and the pump. All ends of tubing were clamped with mosquitoes covered with rubber shods. The prosthesis was placed without difficulty in the left corpora with a 14mm Hagar dilator in the right side to avoid a crossover defect of the prosthetic cylinders. There was no buckling defect and the prosthetic distal tip was noted to be in the mid-glans area. The right prosthesis was placed without difficulty in a similar manner with the identical findings. The corporotomies were then closed with a running 2-vicryl suture with the knots inverted. The pump was placed in a dependent position between the two testicles. A subcutaneous canal was made to the left side of the pubic symphysis and an incision into the rectus fascia was made to develop the sub-rectus pouch for the reservoir. 2-0 vicryl interrupted sutures were pre-placed for closure after the reservoir was placed. The empty reservoir was placed and then filled with 22cc of a 10% Hypaque solution. The reservoir was not palpated through the anterior abdominal wall while inflated. The fascia was closed and the tubing from the reservoir was connected with the tubing from the pump. The prosthesis was cycled through multiple inflation and deflation trials and was noted to correctly function. All tubing was covered with a two-layer 2-0 vicryl closure of the interscrotal connective tissue. The skin was closed with interrupted 4-0 chromic sutures. The bladder was drained and placed on gravity drainage for 24 hours.
The prosthesis was inspected for position, free movement, correct cylinder length and correct inflation and deflation over multiple trials, all of which were normal and adequate. Bacitracin ointment was placed on the scrotal incision and then 4X4 gauze and fluffs were used to bandage the scrotum. An athletic supporter was placed to secure the bandages. The prosthesis was inflated to ? of its full capacity and the pump was deactivated for future activation. Patient was then awaken from anesthesia without complications and transferred to the Recovery Room (RR). The patient arrived to the RR in stable condition and without complications.
To the family and friends of patients undergoing surgery.
SCHEDULED STARTING TIME OF SURGERY:ESTIMATED LENGTH OF SURGERY:
You should plan to check in at the waiting area information desk as soon as your family member or friend has left for the Operating Room. This is the only way we can talk to you afterwards, or on occasion; reach you to give you updates on the operation's progress. If the surgery is scheduled for many hours, you can leave to eat or do other things, but you should let the information desk know that you are going to leave the area, where you are going, and how long you might be gone so that we might reach you if need be. You should be in the area before the elected time of the end of the operation.
The information deck will overhead page you or the "family of" when they receive the recovery call to let you know that the surgery has been completed. The overhead page system works ONLY on the Surgical Waiting Area and not throughout the hospital or the cafeteria.
We will plan to see you in the surgical waiting area after we have safely completed the early phases of the post-anesthesia recovery in the "Recovery Room" or PAR (Post Anesthesia Recovery). This may take up to an hour after the initial call. Sometimes, especially if another case is ready to start, we will call and talk to you. If for some reason, we have not come or called within 30 minutes, please ask the information desk to page us.
Your family member will be in the Recovery Room for 1-2 hours. This is standard recovery time, although the times vary with each individual. For example, spinal anesthetics take longer to "wear off," local anesthetics are much shorter acting. Under no circumstances are family members or friends allowed in the recovery room. The information deck will inform you of the patient's return to the room as soon as they receive the information that the patient has left recovery. At that time, they will give you the room number and direct you to the correct wing and floor.
Activity
Diet
Medication
Catheter and Wound Care
Bowel Movements
When to Contact your Doctor
Contacting Your Physician
Dr. Bauer can be contacted by calling the number listed at the top of the page. You may also call the hospital to have them contact us. Please do not hesitate to call with any questions or concerns.
Frequently Asked Questions after surgery
This section is under construction.