
www.flinturology.com
Urology Services, Inc.
G-1121 West Hill Rd.
Flint, Michigan 48507
Tel: 810.232.8888
Fax: 810.232.9190
Email: jbauer@flinturology.com
[map]
 |
John J. Bauer, M.D.
www.flinturology.com Urology Services, Inc.
|
Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
John J. Bauer, MD, Urologist
Normal Prostate:
Before we begin discussing prostate cancer, it is good to have some understanding of the normal prostate. The prostate gland is about the size of a chestnut. It sits at the opening to the bladder and urine passes through the center of the prostate like the hole in a donut. As we age, the prostate commonly enlarges, closing off the opening and giving the patient difficulty with urination (closing the size of the hole in the donut). This is usually due to benign (NOT cancer) enlargement of the prostate. The prostate is made up of some stromal tissue (the latticework to hold the other cells together), some muscle cells (to contract and push out the fluid it makes), and some cells that make fluid (about 40-50% of the fluid at the time of ejaculation). It is the cells which make this fluid which are the most common to degenerate into a cancer (Adenocarcinoma).
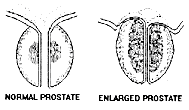
How do you make a diagnosis of prostate cancer:
The two most common reasons for being evaluated are an elevation of the PSA blood test and/or an abnormal feel of the prostate. Abnormalities of these tests suggest that further testing be done. The only way to know if prostate cancer is present or not is to do a biopsy of the prostate and look at the tissue under the microscope. Typically this is done with a needle in the doctors office and usually consists of 10 or more samples of tissue. (See Needle Biopsy of the Prostate). Currently, sextant biopsy is used, taking a core of tissue from the base, mid portion, and apex of the prostate on the right and left side respectively. This gives a fairly good overview of the prostate and how much cancer is present or if it is present at all.
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA):
PSA is an enzyme added to the prostate fluid to help in altering the semen after it is ejaculated. As a rule, it is added to the fluid and therefore drains from the body through the duct system in the prostate. Some of this enzyme backs up into the blood stream and can be measured in the blood. Prostate cancer alters how the cells and duct system configure themselves and therefore cause a blockage to the fluids route of getting out the body. Hence, it tends to back up into the blood stream in higher quantities than in patients without cancer. Having a high PSA is NOT diagnostic of cancer. Today, most patients diagnosed with prostate cancer have been found because their PSA level is elevated.
Digital Rectal Exam:
The rectal exam is an adjunct to the PSA in determining who needs to be evaluated for prostate cancer. (See Prostate Screening). A finger is inserted through the anus, into the rectum to feel the prostate. The normal prostate is rubbery. Most prostate cancers are hard to the touch.
Transrectal Ultrasound:
Ultrasound of the prostate is done with a probe in the rectum and gives a picture of the prostate which is different than that which is felt with the digital rectal exam. It is also used to do the sextant biopsy of the prostate. If there is a lesion noted on the ultrasound which is not felt on the rectal exam, it is included in the biopsy.
NO TEST is always diagnostic. Most patients with an elevated PSA value do not have prostate cancer and thus efforts at refining the PSA test over the years have been looked at, trying to decide who does and who does not need to be biopsied.
PSA Density:
The thought is that patients who have large prostates (benign) should have a higher PSA level than patients with a small prostate since PSA is made by normal prostate cells. The PSA density is calculated by dividing the blood PSA by the size of the prostate as measured by ultrasound. PROBLEM: What is the exact ratio to make this cut off useful. Currently most urologists use 0.10- 0.15, but other values will either increase the number of biopsies done in patients who do not have cancer or suggest no biopsy in patients who do have cancer.
PSA Velocity:
This refers to the rise of the PSA value over time. There is some evidence that patients with prostate cancer have a faster rate of rise than patients without cancer. The current acceptable rise is less than 0.75 ng/ml/year. The PSA's must be done over two years and have at least three values to do this. PROBLEM: This data is obtained from looking at what PSA's did in the past -- therefore do not know if patients who are currently seen with increasing values follow this same trend and is this the best cutoff value -- i.e. should this be a different number, such as 1.0 ng/ml/year.
Age Specific Reference Ranges for PSA:
The theory is that younger males should have smaller prostates, therefore, lower PSA values and older males, and therefore may have higher PSA values. Current values are a PSA value less than 2.5 for patients in their forties, 3.5 for patients in their fifties, 4.5 for patients in their sixties and less than 6.5 for patients older than this. PROBLEM: It skews the data so that younger men are evaluated who do not have prostate cancer while not evaluating some older men who do have prostate cancer.
Free/ Total PSA Ratio:
PSA occurs in at least six forms -- one not bound (free or non-complexed) and five bound to some proteins (bound or complexed). The ratio is obtained by measuring the percent of free to total PSA. As a rule, more PSA is free in patients with benign disease and complexed in patients with prostate cancer. PROBLEM: What is the cut off for the ratio? The lower the percentage, the more patients are evaluated who do not have cancer, while increasing the value does not catch some patients who have cancer and are not biopsied.
Who Needs To Be Biopsied:
As a rule, patients with an abnormal digital rectal exam (lump noted on the prostate gland), elevated PSA values, increased PSA-Density, increased PSA-Velocity, % Free PSA less than 25%, and patients with an abnormal bone scan need to have a biopsy done on their prostate.